Kaizen is a manufacturing philosophy in Japan that has been applied for centuries and is still playing a key role in improving cost efficiency for many small and large businesses around the world.
In the 1993 edition of the dictionary “The New Shorter Oxford English Dictionary”, besides the definition “is the continual improvement of the working process, the improvement of productivity, etc”, “Kaizen” also means “Improving the quality of personal life, family relationships, social relationships and working environment. When Kaizen is applied in the workplace, it means continuous improvement that concerns everyone – the leadership as well as all employees.”
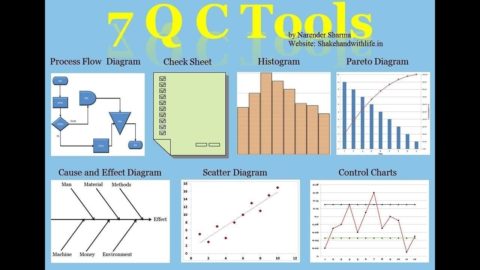
To do Kaizen, you only need common, simple techniques like 7 quality control tools (Pareto chart, cause and effect chart, control chart, scatter chart, graphs and checklist) investigation).
Here are a few examples of statistics in some typical businesses:
At Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Kaizen penetrates every corner of manufacturing activities, from making space missiles to assembling aircraft. The result is faster, cleaner and more efficient production, lower inventory levels, and lower costs.
Take the example of Toyota – a very successful business in implementing Kaizen: A typical innovation of Toyota is in the freight car – the type of transport within the factory. Before Kaizen, Toyota had to spend a large amount of money to buy them. But then, it was discovered how to build this vehicle by adding engines to parts available on the production line. That way, the cost of shopping for a freight car is reduced by more than half, resulting in a savings of nearly $ 3,000 per vehicle – a savings worth learning. By using plastic baskets to sort parts by car model, workers do not spend time sorting by characteristics. At Toyota, kaizen is one of the core principles of the Toyota Production System, a mission of continuous improvement and a single word that sums up Toyota’s slogan: “Always a better way”.
At Nam Ha Garment Joint Stock Company, the company has reduced the percentage of defective products from 8.8% to 8.1%; 25% off inventory on line; inventory against production capacity decreased from an average of 2.37 days to 1.34 days; Along with that is the average output increased from 415 products / day to 899 products / day.
At Google, employees spend 10% -20% of their time figuring out better ways of doing things and the remaining 80% working. Google is constantly coming up with new ideas to improve the quality of work.
Poductivity and Quality Office