
Illustration (Source: Internet)
The factory produces mechanical parts with medium scale with 7 areas A, B, C, D, E, F & G. The factory works 2 shifts / day, 8 hours per shift and an average of 96 workers each shift. During the production process, raw materials / semi-finished products / finished products are moved by trolleys. The monthly salary for trolley operators is 10,000 Rupi / month; The number of people operating the cart is 4.
The current layout of the plant is currently not in optimal use of resources. Therefore, the need to improve the layout to reduce material distribution costs and increase productivity. In this case, a moving chart analysis technique was used to determine the material distribution costs between areas.
Areas in the factory:
(A) Storage of raw materials and finished products.
(B) Group 1 includes: 3 automatic lathes, 1 hole boring machine, 2 drilling machines and 1 turret lathe.
(C) Group 2 includes: lathes, drills, milling machines and small cutting machines. This area is used to process small parts.
(D) Group 3 includes: milling machines, drills and grooving machines.
(E) Group 4: milling machines.
(F) Assembly teams: All parts machined in the above groups are assembled and assembled together to form the final product.
(G) Packaging department.
The process of factory layout
1) Collect detailed information about products, processes, etc. and systematically record data.
2) Analyze data using various analytical techniques.
3) Choose a general flow model for materials.
4) Designing individual work stations
5) Assemble the individual stations into the overall layout according to the general flow model
6) Complete factory layout.
Tools and techniques for factory layout
The amount and quality of data on various factors is needed to develop a good site. Data will be collected relating to different processes, operation sequences, frequency of material flow, and space.
The following tools and techniques are used for data analysis.
– Process maps
– Movement chart
– Flow diagram and sequence diagram
– Relationship charts
– Time study data
Analysis of plant layout
The most important criterion for analyzing and selecting the plant layout is the cost of material distribution. The primary tool used to analyze material distribution costs in site layouts is a moving chart. Depending on the existing site layout, the analyst may follow the procedure outlined below:
1) Step 1. Summary of movements in existing premises
2) Step 2. Simplify by considering the movement of materials between any two areas.
3) Step 3. Prepare the material distribution matrix of the current site.
4) Step 4: Calculate the total distribution cost of materials by the existing premises.
5) Step 5: Look for changes that may reduce travel distances and then recalculate the total material distribution costs.
A. Calculate the cost of material distribution with the current premises
1) Arrangement of existing premises
a) The total distance traveled by handcarts between areas in the factory
= 9322 m / day
= 9322 m / 2 shifts
= 4661 m / shift
b) Material distribution cost per meter of movement
= Labor cost per shift / Travel distance per shift
= (4 * 10,000 / 30) / 4661 = 0.2861 Rupi / m
c) Raw material distribution cost per day
= 9322 m / day * 0.2861 Rupi / m
= 2667 Rupi / day
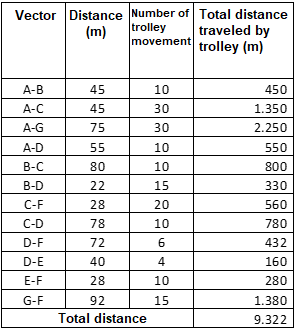
Table 1: Material movement distance with current ground layout.
B. Calculation of material distribution expenses with ground plan No. 1:
Areas F and G are interchangeable, other areas remain the same. Then:
a) The total distance traveled by handcarts between areas in the factory is: 9040 m / day.
b) Cost of material distribution per day are:
= 9040 m / day * 0.2861 Rupi / m
= 2586 Rupi / day
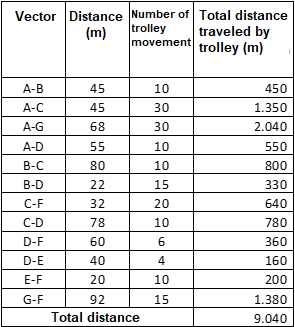
Table 2: Analyzing the distance of moving materials with the ground layout according to plan 1
C. Calculation of material distribution expenses with ground layout plan No. 2:
Swap C and G, the other positions remain the same as Option 1 and the number of moves between locations remains constant. Then:
a) The total distance traveled by handcarts between areas in the plant is 8540 m,
b) Costs of material distribution per day are:
= 8540 m / day * 0.2861 Rupi / m
= 2443 Rupi / day
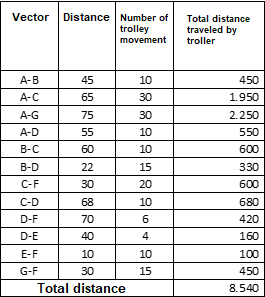
Table 3. Analyzing the distance of moving materials with the ground layout according to plan 2
Conclude
By using the moving chart analysis technique with cost-saving criteria, two options of site re-arrangement have been proposed. Option 1 helps to reduce 81 Rupi / day and Option 2 helps reduce 224 Rupi / day. The company can choose the option that suits the actual operating conditions to reduce material waste transportation, thereby spending time increasing activities that bring added value.
Productivity and Quality Office