
Illustration (Source: Internet)
OEE is a measurement index used in TPM to indicate the level of effective operation of machinery. This index is given by a Japanese expert, Mr. Seiichi Nakajima.
During the TPM implementation steps at the enterprise, the overall equipment performance (OEE) evaluation is always given special attention. Put simply, OEE is a measure of equipment performance and plant productivity. Factors such as the availability, efficiency rate and output quality ratio of an equipment or production line are reflected by OEE through actual production performance data compared to expected.
OEE is a central element of TPM, although the role of OEE in enterprises is not the same. Measuring OEE values is helpful in identifying sources of losses to overall performance. Based on the evaluation of this indicator, the manufacturer can find out the cause and location of the damage, thereby providing corrective measures and continue monitoring until the overall performance is improved.
OEE can be considered as an effective methodology to measure efficiency in factory processes. OEE is the main performance indicator for Total Productivity Management (TPM), and also for IATF 16949. OEE is used in smart factory software, following the trend of industrial revolution 4.0.
How to calculate OEE?
According to the formula, OEE is calculated based on three coefficients: A – Availability – Machine readiness factor compared with the estimated time of running the machine (usually in a day, or in a production shift); P – Performance (yield coefficient); Q – Quality factor
OEE = Ax P x Q
Example of calculating OEE in a production shift for an individual machine.
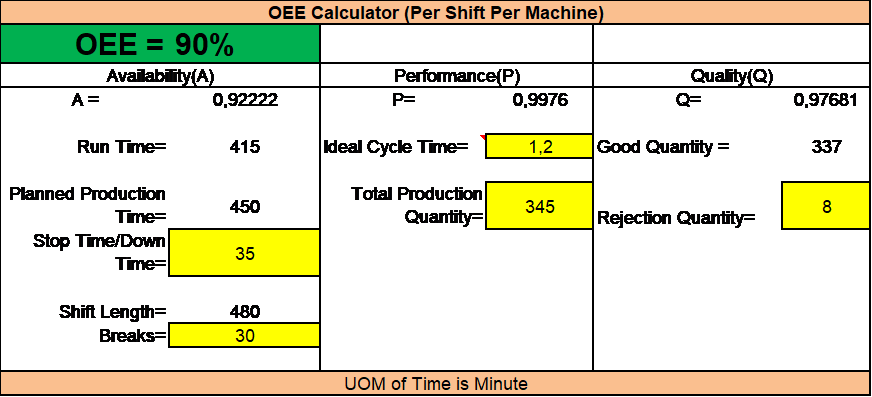
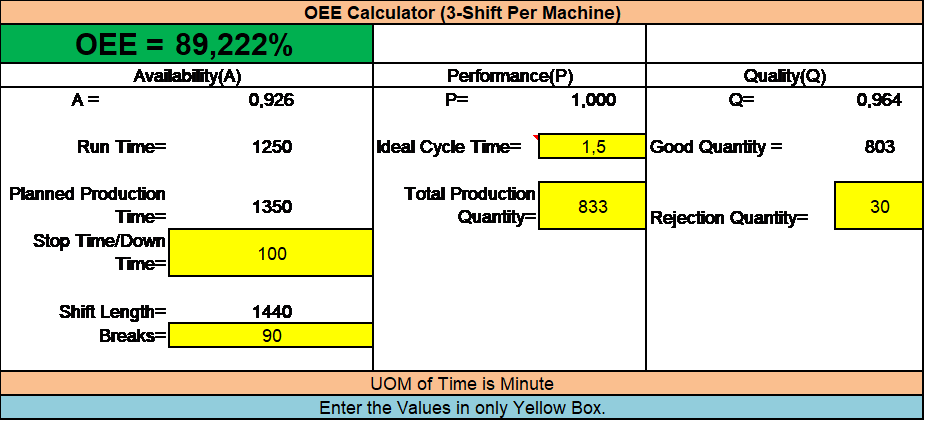
And below is example of calculating OEE in 3 pro duction shifts/per day for an individual machine.
Here’s how to calculate OEE in the above two cases: Using the excel file similar to the above interface, enter the number in the yellow highlighted part:
Example of calculating OEE in a production shift for an individual machine
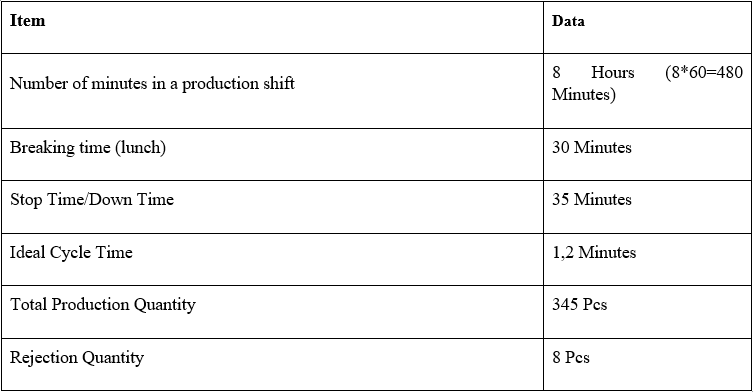
Based above data, we can calculate OEE (01 shift for 01 machine) = 90%
OEE = A x P x Q = 92% x 99,76% x 97,68%
Example 2: example of calculating OEE in 3 production shifts/per day for an individual machine.
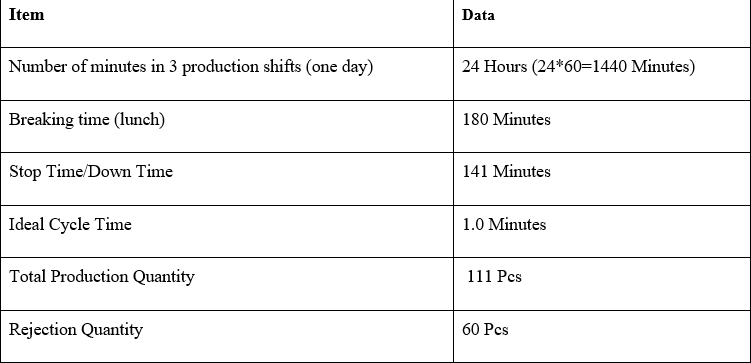
Based above data, we can calculate OEE (03 shift for 01 machine) = 89,2%
OEE = A x P x Q = 93% x 100% x 96%
For other calculation cases, readers can calculate or contact the Support Program of the Department of Science and Technology, Ministry of Industry and Trade (MOIT) for guidance and support, via email: vanphongnscl@gmail.com.
Productivity and Quality Office