A case study conducted by Vipulkumar C. Patel and Hemant Thakkar showed that a good application of 5S at a ceramic kiln can bring many outstanding benefits to producers.
The goal of the plant when participating in research is to find a solution to reduce the amount of technology waste, while keeping waste at a low level. On the other hand, the factory managers also shared that they need a tool that helps shorten the quality control process, improve warehouse space, reduce errors and improve internal safety standards.
For a large-scale and highly automated ceramics factory, the potential for improvement is more limited than for a small and medium-scale production facility where there are many manual processes. To achieve the required plant efficiency, the team of experts surveyed the field to capture visual images of the location to be improved, and studied the technology diagram to come up with the right solution. At the end of this process, the team decided that the 5S application would be done at the warehouse division and the insulating porcelain production department.
Common mistakes here include: The warehouse of raw materials, semi-finished products & finished products is too much and takes a long time to load and unload; There are many unnecessary and unorganized items and moving objects requires a lot of travel and long distances. Immediately after completing the first 3S of 5S, the warehouse division saves 12.91% of space and minimizes waste. At the same time, the productivity of the insulating porcelain production department has also increased.
Here’s what the factory did:
A. Screening: In the beginning, the warehouse looks very unorganized and cluttered. Figure 1 illustrates red plates attached to unnecessary supplies. The purpose of this is to identify unnecessary items that take up space in the warehouse. The strategy is to create more space by better organizing the location of items and equipment in the warehouse and eliminating unnecessary items. After removing items and equipment with the red plate attached, warehouse space is expanded. These spaces will be reserved for commonly used supplies or transportation paths in the warehouse.

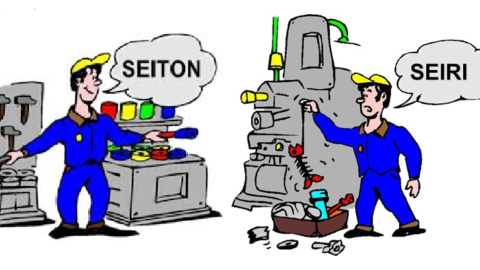
B. Sorting: The next step after removing unnecessary items is to arrange the rest of the objects to suit the work needs of each area. During this process, try to arrange objects in a visible position to make it easier for management and workers while working. Figure 2 shows the difference before and after applying 5S at warehouse. In Figure 3, the working area is on the outside of the road divided by black yellow lines. This is the path of people, materials and equipment in the workshop, which ensures easier movement and minimizes product damage and accidents.

It can be said that the first 2S in the 5S laid down a solid foundation to help the factory more favorable in the standardization process later. S3, S4 and S5 will be described in detail in the following section.

(To be continued)
Productivity and Quality Office